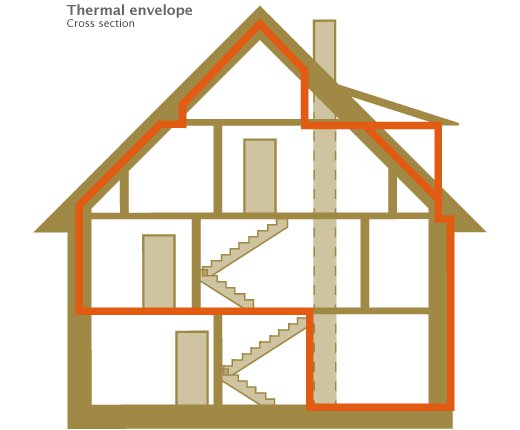
Ceilings and roofs can account for 25% to 35% of heat loss, Wall account for 15 to 20%, floors account for up to 10 to 20% of heat loss. Care should be taken to also insulate floors as well as edges of ground slabs. The heat flow through the building’s envelope can be improved or controlled by adding a layer of thermal insulation to the exterior of the building components such as walls, roof, and floor. These materials are of low density and lightweight. Some insulation materials are filled with special gases, which have higher a higher resistance to heat flow than air. Insulation materials can come in various forms whether mineral synthetic / petrochemical or natural materials. Mineral wool is a common insulation material (can be clicked upon for more information, see text box below) used for buildings and a number of other typical insulation materials exist, including aerated concrete, cellular glass, expanded and extruded polystyrene (EPS and XPS), polyurethane, cellulose fibres and fibre boards. More innovative insulation concepts include the dynamic insulation that has been in use in Scandinavia and Austria for some time as well as transparent and translucent insulation and vacuum insulation panels and nano fibres.